Fire is nothing less than brilliant and has been an asset to the human species for thousands of years.
However, it is not all that convenient. Sometimes fire breaks out when least expected, threatening lives, properties, and everything you hold dear. Wouldn’t it be incredible if the fire was as simple to control as electricity, so people could switch it on/off at a moment’s notice?
Well, that’s the basic concept behind heating elements. They are the “fire” inside such products as electrical heaters, clothes dryers, hairdryers, stoves, and all sorts of household appliances. One common question regarding heating elements is the effects of the number of coil turns.
In most cases, a typical heating element refers to a coil, ribbon- straight or corrugated- or a strip of wire that radiates heat much like a lamp flame.
When an electric current flows through it, it glows intensely red hot and converts the electrical energy going through it into heat, which radiates out in all directions.
Now that you understand what household elements are, you’re probably wondering about the effects the number of coil turns on the appliance.
Table of Contents
4 Turn vs. 5 Turn Heating Element: What You Need to Know
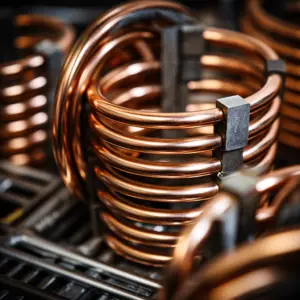
In simple terms, more coils mean better heat distribution. More impact areas often reduce the chances of hot spots. However, the fact that the manufacturer can adjust the size of the internal heating element and modify its alloy, the length of the element does not always relate to power.
In terms of cooking, it’s mostly just surface area. A greater number of coil turns means that you’ll have more surface area and even more heating of the pan. So, the number of coils does make a minor difference in the overall time it takes to heat the burner.
Speaking of 4 Turn Vs 5 Turn Heating Element, the one with extra coils will usually have smaller and therefore heat faster and cool faster. The extra turns make up for the smaller coils. As a result, 5 turn heating elements are likely to offer better heating performance compared to 4 turn heating elements.
That said, it’s important to look at the ratings of the different coils. Do they have the same wattage? Are the connections the same? These factors dictate the performance and suitability of the heating element.
There are also specific factors that should be considered for each different type of element. For instance, with 4 turns coiled elements made of round wire, the diameter of the wire, and the form of the coil (length, pitch, diameter, stretch, etc) are among the things that critically affect the performance.
Likewise, with a ribbon element, the ribbon surface area, thickness, width, and weight all have to be factored in.
Does Heating Element Need High or Low Resistance?
It’s easy to think that a 4 turn or 5 turns heating element would need to have a really high resistance- given that it’s the resistance that enables the material to generate heat. However, that’s not exactly the case.
What produces heat is the current traveling through the element, not really the amount of resistance it feels. In fact, it’s much more important to get the maximum current flowing through your heating element than forcing that current through a large resistance.
Types of Heating Elements
There are many different kinds of heating elements. Sometimes manufacturers use bare nichrome, as it is, and other times it’s embedded in a ceramic material to make it more robust and durable. Remember ceramic is great at coping with extreme temperatures and doesn’t mind lots of heating and cooling.
The shape and size of a heating element are largely determined by the dimensions of the appliance it has to fit and the area over which it is intended to produce heat. The heating elements are very visible in sole appliances. For instance, in an electric toaster, you can easily spot the ribbons of nichrome built into the toaster walls because they glow red hot.
Electric radiators produce heat through glowing red bars, which are essentially coiled, wire heating elements that give out heat by radiation. Meanwhile, electric convector heaters typically have concentric circular heating elements placed in front of electric fans.
Still, some appliances such as electric kettles generally have visible elements that work at lower temperatures and don’t glow, as they never need to operate above the boiling point of water.
Other appliances may have heating elements completely concealed, mostly for safety reasons. These include things such as showers and hair curling tongs. They’re designed with concealed elements to tone down the risk of electrocution.
How to Replace a Heating Element
If you want to replace a water heater, make sure you replace the rubber seal to prevent leakage. Put a gasket on the threads of the threaded element or around the base of the element.
Then install the new element with a gasket in place by reversing the removal process and turning the element clockwise.
How to Replace a Stove Element
When replacing a stove element, put a piece of paper on the glassware. Firmly grip the glass bowl with both hands and turn it, and then place the glass plate on the stove. The foil will protect the surface of the glass plate when your heating element is replaced.
Can You Replace a Heating Element in an Oven?
It is easy to replace a heating element on a grill or baking in the oven. It shouldn’t take you more than an hour, as you can change the items from inside the oven without having to remove the oven or even move it.
Moreover, you don’t have to replace the heating element in your oven very often. Note that the heating element is an old and sturdy element that rarely needs to be replaced before the rest of the unit breaks down.
That said, however, if you have an overheating element that requires replacing, then you can always replace it.
